Cyber Risk Management Made Simple for SMBs
Why Cyber Risk Management Matters for Small & Mid-Size Businesses
Cyber risk isn’t just an IT problem—it’s a business risk. For SMBs, a single ransomware attack or vendor breach can stall operations, drain revenue, and erode customer trust. Practical cyber risk management helps you prioritize what matters, invest wisely, and keep your business running.
4 Real-World Impacts of Cyber Attacks
• Systems downtime and delayed orders or services
• Financial losses (fraud, lost sales, fines)
• Data exposure or theft
• Loss of customer, partner, and employee trust
The Cyber Risk Management Process
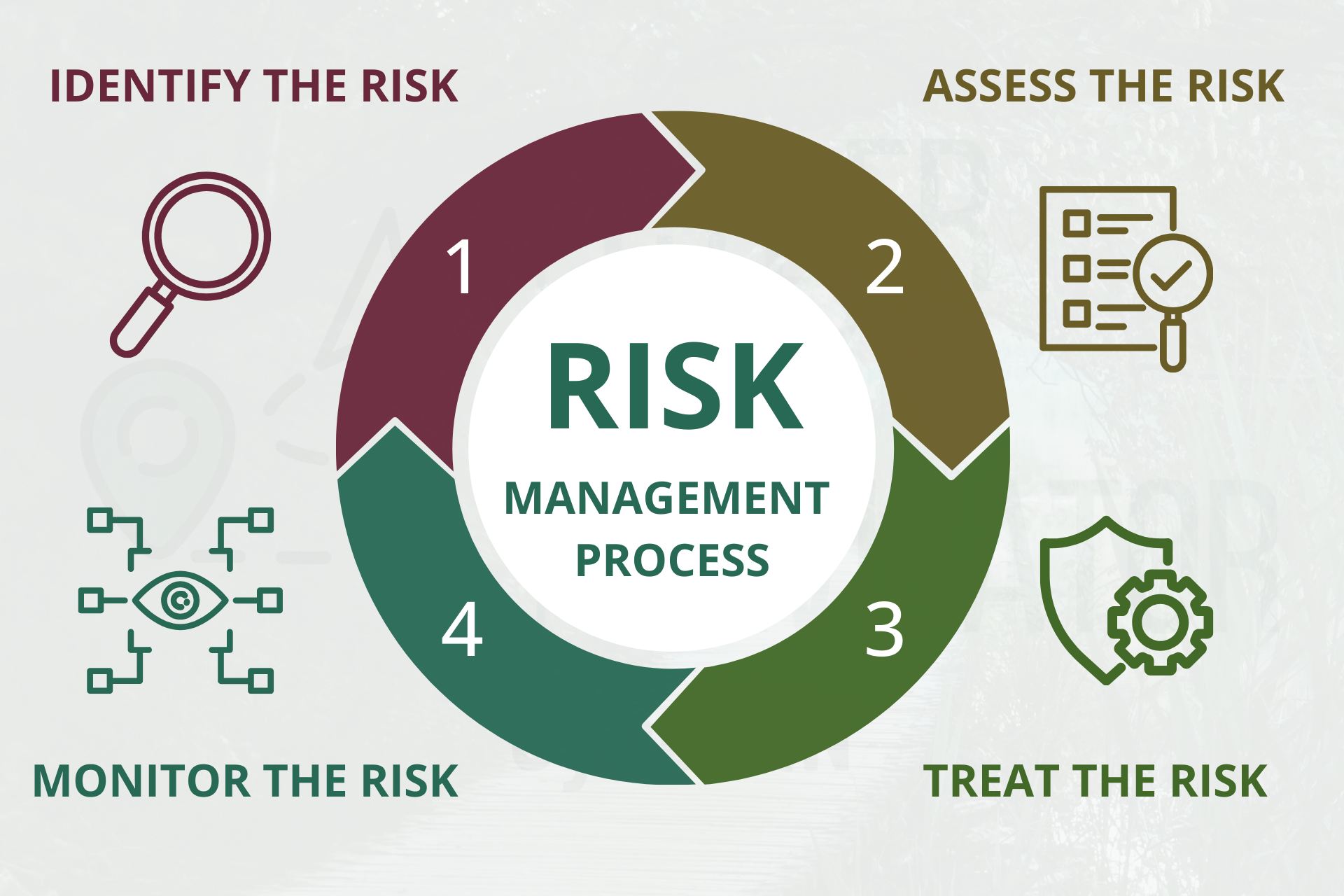
A cyber risk management process is the structure businesses use to manage cyber risk consistently over time. It gives leadership a repeatable way to set priorities, assign ownership, and track progress. A practical process many organizations follow includes,
1) Identify
List critical assets (POS, EMR, CRM), sensitive data (PII, PHI), and high-risk vendors. Map where data lives and who touches it.
2) Assess
Estimate likelihood and impact for top threats (phishing, ransomware, misconfiguration). Document current controls, owners, and gaps. Produce a short, prioritized risk list—not a long shelfware report.
3) Respond
Choose one of four responses for each risk: reduce (add MFA, backups), transfer (cyber insurance, contracts), accept (with documentation and review date), or avoid (change the activity). Align responses with budget and business goals.
4) Monitor & Review
Risk changes as the business grows. Track control effectiveness, vendor changes, incidents, and new tools. Review quarterly; adjust owners and priorities.
5) Continuous Improvement
Use incident reviews and threat intel to refine safeguards. Turn lessons learned into a practical quarterly roadmap.
Which Cybersecurity Risk Management Framework is Best for SMBs?
The best risk management framework is one that allows flexibility and scales to your unique business requirements. Any of the frameworks below can be adopted to fit where you are in your risk management journey.
NIST Risk Management Framework:
Developed by the National Institute of Standards and Technology, this framework integrates security and risk management into the system development lifecycle, ensuring that security considerations are embedded in all phases of operations.
ISO 31000:
This international standard provides guidelines for risk management applicable to any organization, emphasizing the integration of risk management into governance and decision-making processes.
COSO Framework:
Focused on enterprise risk management, COSO provides a comprehensive approach to managing risks that could affect an organization's ability to achieve its objectives.
FAIR (Factor Analysis of Information Risk):
This framework is particularly useful for quantifying and analyzing information risk, helping organizations make informed decisions about risk management.
The key is adopting a version that is aligned with your business goals.
Next Steps: Know Your Business Risks with Cyber Risk Navigator
Cyber risk management works when it leads to decisions your business can act on. Book a consultation with Cyber Risk Navigator to get a concise, prioritized risk plan aligned to your budget and goals.